Thanks to a new US research, plant waste can become the source of the aromatic components of SAF
New route for a sustainable aviation fuel that does not require the help of kerosene
(sustainabilityenvironment.com) – What is Sustainable Aviation Fuel? They are called the SAF and are the most viable strategy of decarbonization fielded by aviation. Behind the three letters are hidden the words sustainable aviation Fuels, that is sustainable aviation fuels, mixtures able to lower the carbon footprint of the sector while waiting for new propulsion technologies with zero emissions.
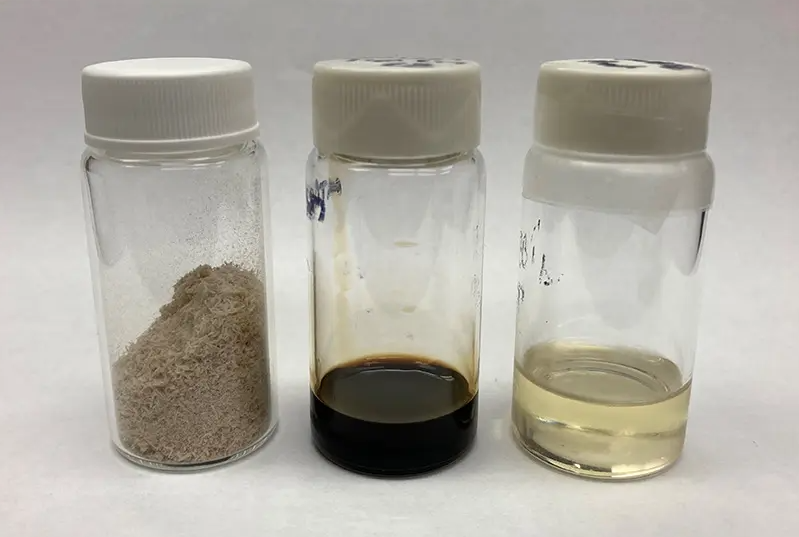
Currently, there are 7 types of biofuels (only one of industrial level) whose use, in a mixture of up to 50% with fossil kerosene, has been approved and meets the requirements of technical standards of aviation. But the objective of the section is always to bring the quota to 100%. This could be made easier by research conducted by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Washington State University. Scientists report that they have used lignin – the organic polymer that gives rigidity to plant cells – as a tool for 100% sustainable aviation fuel.
How sustainable aviation fuel is made? How is SAF produced from lignin?
Jet fuel is a mixture of several hydrocarbon molecules, including aromatic and cycloalkanes. Current industrial technologies for the production of SAF are not able to equip biofuels with essential aromatic molecules, making mixing with conventional hydrocarbon fuels mandatory. “Being the largest source of renewable aromatics in nature, lignin could be the answer to getting a full biological-based aviation fuel,” NREL writes in a press release. Obtaining such compounds has always been a difficult process. To jump the obstacle, the team developed a two-stage continuous catalytic process using molybdenum carbide to deoxygenate lignin to aromatic hydrocarbons. “Other processes have been attempted to reduce the oxygen content, but the catalysts involved require expensive noble metals and have proven to be low yield”.
Read also The first A380 powered by 100% sustainable aviation fuel takes flight
Tests on fuel properties have shown that aromatic compounds derived from lignin are also likely to have performance advantages over aromatic compounds of conventional jet fuel. The results were published in the journal Joule.