According to the Digital City Index 2022, it is the involvement of citizens in the digitalization process that ensures the success of projects.
Investments in smart cities will reach USD 327bn in 2025
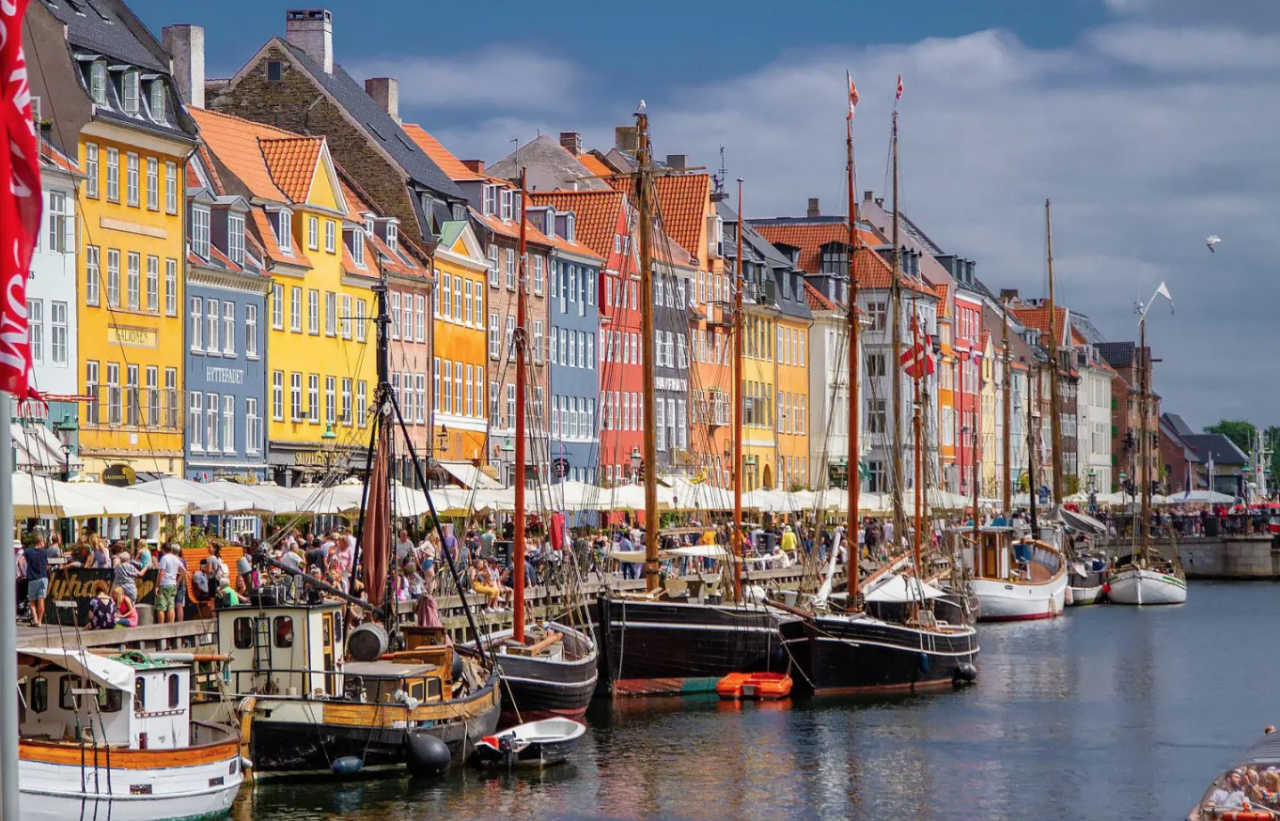
(Sustainabilityenvironment.com) – According to Economist Impact’s Digital City Index 2022, Copenhagen is the smart city that has launched the world’s most successful digital transformation. Follow Amsterdam, Beijing, London and Seoul. The only Italian city on the list of 30 analyzed is Rome, with a decent 21st place.
Developed with the collaboration of NEC, the report takes into account four key pillars of analysis: digital connectivity, services, culture and sustainability. Each city in the list is then awarded a score for each item, coming to define the podium for each of the four themes and in the general ranking.
According to the authors of the report, the success of the projects is mainly determined by the involvement of citizens in the design of smart cities. The last decade in particular has marked great strides in digital infrastructure, providing municipalities with a suite of extremely important features to develop safer, cleaner, smart and inclusive cities. Artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, 5G connectivity, e-mobility, up to digital currency, are just some of the items on the list.
According to current estimates, investments in smart cities will reach 327 billion dollars by 2025. Starting from just over $96 billion in 2019. The biggest expenditure in smart technology will come from the US, Western Europe and China. The decisive push came mainly as a result of the problems triggered by climate change and urban population growth.
The Four Pillars of the Digital City Index
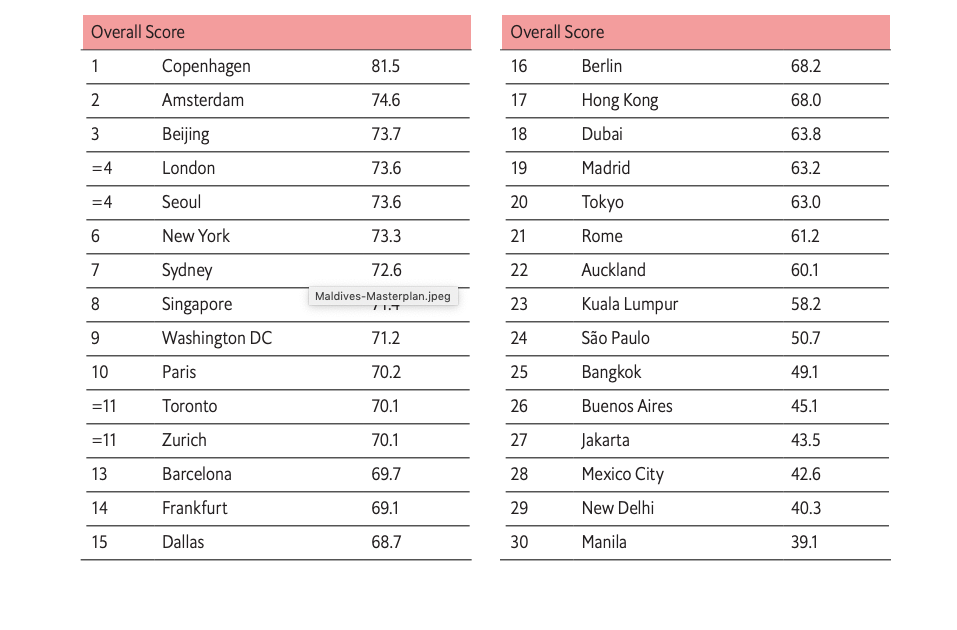
According to the Economist Impact report, the top cities are those that have set clear and achievable goals. For European cities this has mainly been about successes in smart mobility management. While in the case of Beijing and China, success has been achieved in applied technology to address problems such as pollution or the sharing economy. “Smart cities will be safer, cleaner and more inclusive urban landscapes, where citizens will enjoy better public health and services, more efficient transport and important economic improvements to be shared as public goods,” the report stresses.
Sustainability
Urban sustainability was the most impactful area of the Report. Leading the partial ranking of smart cities are Copenhagen, Seoul and Toronto, cities that have been able to use digital technology to improve the intelligent management of utilities. So IoT sensors, AI, and technological innovation have made it possible to improve energy efficiency, use fewer resources, or manage waste better. Many emerging-market cities have ranked below average. Only Beijing maintained a 5-place finish, above Amsterdam, Sydney and London, thanks to the efforts made to fight the historical challenges of air pollution. “The involvement of citizens is crucial to make the next wave of innovation in the digital city effective and accepted”.
Read also AIoT, when Artificial Intelligence rules the IoT in smart cities
Culture
The Digital City Index analyzes this pillar from the perspective of value-based performance, and government engagement. On digital inclusion and citizens’ confidence in governance. In this case, it is emerging markets, such as Asia, that have higher levels of skills and satisfaction with e-governance. Probably due to the lack of physical services that are easy to access, especially in poor geographical areas.
Services
The efficiency of the services of the municipalities detected by the Digital City Index, in this case, goes to analyze the quality of digitalization offered. The use of digital identities, transportation apps, and biometric identification for health or education are just some of examples.
Singapore, Sao Paulo and New Delhi ranked first in the provision of digital municipal services. While New Delhi is in third place mainly thanks to the success of Aadhar, the country’s revolutionary national scheme of digital identity.
A particular case is that of Seoul, which through the metaverse, will offer its citizens easy access to government services.
Connectivity
Too many cities are still poorly connected, creating a gap between the wealthiest and the poorest. However, the pandemic has prompted many cities to adapt to new needs, also starting telemedicine courses. Also in this case it is Copenhagen leads the ranking, followed by Singapore, Zurich, Beijing and Sydney.













