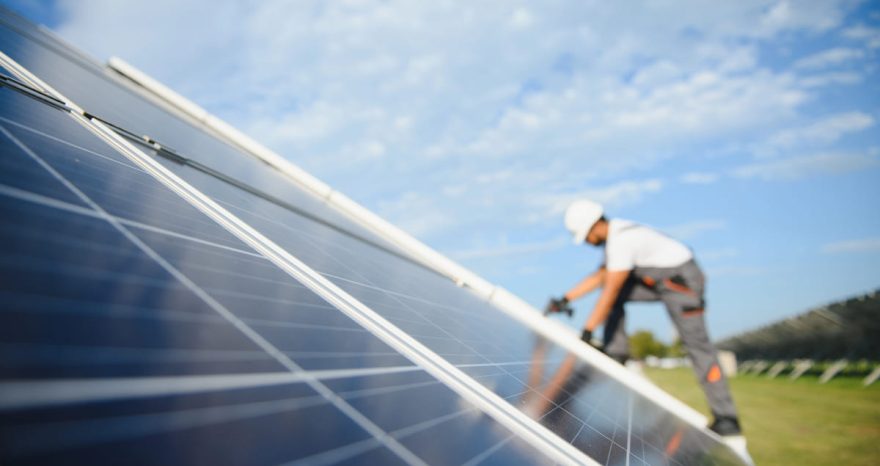
A survey by the Bureau of Investigative Journalism reveals that suppliers of major meat processing brands, such as Cargill and JBS, make excessive use of a class of antibiotics that the WHO classifies as of "critical importance" to human health. Facilitating the emergence of bacteria resistant to these products and therefore more dangerous to humans
Antibiotic resistance is the cause of death for 33 thousand people every year in Europe
(sustainabilityenvironment.com) – The US suppliers of large global meat brands such as McDonald’s, Walmart or Taco Bell make excessive use of a type of antibiotics crucial for the treatment of many bacterial infections in humans. Quantities so high that bacteria can develop antibiotic resistance and endanger human health. This is supported by an investigation by the Bureau of Investigative Journalism.
The class of antibiotics under the lens is the HP-CIA, that is, the one declared by the World Health Organization as “antibiotics of critical importance“. So important that the UN agency warned that their use in animal husbandry should cease altogether. The risk, in fact, is that these products become useless to cure humans if bacteria begin to develop resistance to antibiotics.
Despite the UN request, data from the US Department of Agriculture on the 10 largest groups involved in transforming meat speak for themselves. In all their suppliers there is evidence of the use of at least one HP-CIA. But in some cases, as with JBS, up to 7 were found at the same time, while suppliers of another large meat brand like Cargill use up to 5 of them together.
The spread of drug-resistant bacteria in the environment poses a huge public health challenge because it “creates an inexorable cycle of escalation,” says Dr Sameer Patel, an infectious disease specialist at Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago. “You have to use stronger antibiotics because you don’t want the patient to get more sick and die. And then you use these more powerful antibiotics and eventually the patient becomes resistant to those antibiotics“.
Antibiotic resistance is the cause of the deaths of about 1.3 million people every year worldwide. In the European Union, according to data from the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net), more than 670 thousand infections occur each year due to antimicrobial resistant bacteria (including antibiotics)And that about 33,000 people die as a direct result of these infections. In the United States the annual deaths attributable to this cause would be about 35 thousand.