Perovskite-CIGS tandem solar cells reach record efficiency
A new world record for flexible solar technology comes from South Korea. Researchers at the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) have developed lightweight tandem perovskite-CIGS solar cells with the highest conversion efficiency ever recorded for this category: 23.64%. The result marks a breakthrough with promising implications for aerospace integration.
Tandem perovskite solar technologies evolving beyond silicon
When it comes to tandem perovskite solar cells – a class of next-generation photovoltaic materials – the most well-known pairing has been with silicon. That combination dominated early research due to silicon’s industrial leadership and rapid scientific development. Today, perovskite/silicon tandem cells are already entering commercial production, with conversion efficiencies rising steadily.
The highest recorded for large-area devices (9 cm²) belongs to CEA-3SUN with 30.8%, while for small-area devices (1 cm²), LONGi Solar holds the record at 33.9%.
However, the field has been expanding to explore new pairings. Thanks to the tunable bandgap of perovskite materials, researchers can now design tandem cells fully based on perovskites or combine them with other semiconductors to optimize performance across different wavelengths.
One of the most promising pairings is with CIGS – copper indium gallium selenide – a material known for its use in flexible thin-film solar modules.
Pushing perovskite-CIGS tandem cells to new heights
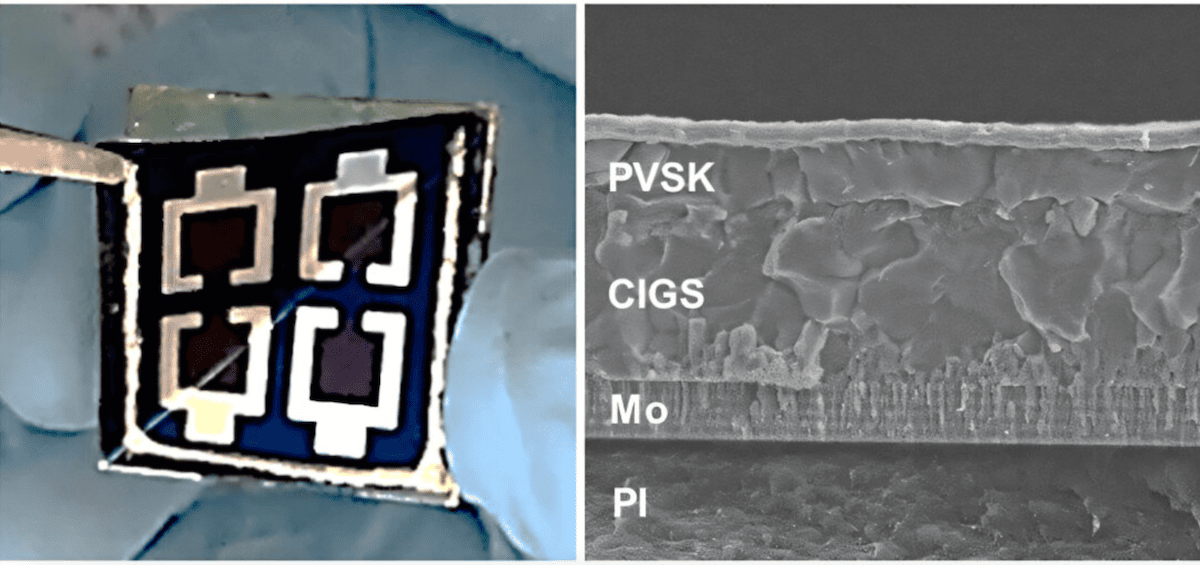
Until recently, perovskite-CIGS tandem solar cells had lagged behind their silicon-based counterparts in performance and scalability. But that may soon change. KIER’s research team developed a new fabrication method to transfer ultra-thin CIGS films onto lightweight, flexible substrates.
Instead of building directly on flexible polyimide, the researchers first deposit a polyimide layer onto a rigid glass base. They then fabricate the tandem solar cell on top and later separate it from the glass.
This technique allows for a more stable manufacturing process and ensures uniform layer deposition, improving overall device performance and reproducibility.
“CIGS films grown on polyimide-coated glass showed larger grain sizes, higher carrier concentrations, and reduced charge recombination compared to films grown directly on bare glass,” the study notes, published in Joule.
High power-to-weight ratio and mechanical durability
The new perovskite-CIGS solar cell achieved a conversion efficiency of 23.64%, significantly outperforming the previous record of 18.1% for flexible devices in this category. Even more impressive is its power-to-weight ratio of 6.15 W/g, making it highly suitable for aerospace and other structural applications.
To assess durability, the researchers tested the material’s mechanical properties and simulated the stress it would face during bending. After 100,000 bending cycles, the cells retained 97.7% of their initial efficiency.
The research, “Flexible and lightweight perovskite/Cu(In,Ga)Se₂ tandem solar cells”, was published in Joule (2024).